Porters 5forces
An In-depth Analysis of Porter’s Five Forces Model: Understanding Competitive Forces in Business
Porter’s Five Forces model, developed by Michael E. Porter in 1979, is a widely recognized framework for analysing competitive forces within an industry. It provides a systematic approach to understand the factors that shape competition and influence the profitability of businesses operating in a specific market. The model examines five key forces that collectively determine the attractiveness and intensity of competition in an industry. This article explores each force and its implications for businesses seeking to gain a competitive advantage.
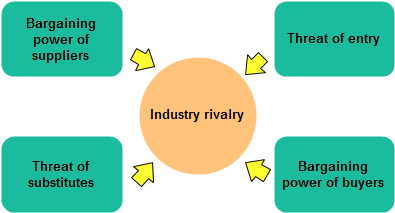
1. The Threat of New Entrants
The first force in Porter’s model deals with the potential of new competitors entering the market. When barriers to entry are low, new players can easily enter the industry, increasing competition and potentially driving down profits for existing companies. These barriers may include economies of scale, brand loyalty, access to distribution channels, government regulations, and high capital requirements. Established companies must continuously innovate and maintain customer loyalty to deter new entrants from gaining market share.
2. The Bargaining Power of Suppliers
The bargaining power of suppliers refers to the ability of suppliers to influence the terms and conditions of a transaction. When suppliers have significant control, they can raise prices or reduce the quality of their products, impacting a company’s profitability. Industries with a limited number of suppliers or unique resources may experience higher supplier power. To mitigate this force, companies can build strong relationships with suppliers, seek alternative sources, or vertically integrate their supply chains.
3. The Bargaining Power of Buyers
On the flip side, the bargaining power of buyers represents the influence customers have on businesses. When buyers have numerous choices or can easily switch to alternatives, they gain leverage to demand lower prices or higher quality products and services. Industries with standardized products or high buyer concentration typically face stronger buyer power. To address this force, companies must focus on differentiation, customer satisfaction, and building brand loyalty to retain their customer base.
4. The Threat of Substitute Products or Services
Substitute products or services pose a risk to companies within an industry. If customers can find alternative solutions that satisfy their needs at a lower cost or with better features, the demand for a particular product or service will decrease. Industries with many close substitutes face higher competition and need to invest in product innovation and marketing to differentiate themselves effectively.
5. The Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
The final force in Porter’s model examines the degree of rivalry among existing competitors. Highly competitive industries, with numerous players of similar size and power, often experience price wars and aggressive marketing campaigns. This intense competition can negatively impact profitability for all firms involved. Companies must focus on their unique selling propositions, market positioning, and strategic alliances to gain a competitive edge and survive in such environments.
To get the best out of Porter’s Five Forces analysis, follow these steps:
6. Thoroughly Research and Identify Key Forces:
Conduct comprehensive research to identify the key forces at play in your industry. Understand the specific factors influencing each force and their impact on your business. Gather data, conduct surveys, and analyse industry reports to get a clear picture.
7. Stay Updated with Market Trends:
Keep abreast of market trends and changes that could affect the industry forces over time. Market dynamics are continually evolving, and staying informed will help you adapt your strategies accordingly.
8. Conduct a Competitor Analysis:
Analyse your main competitors using the Five Forces model. Understanding their strengths, weaknesses, and market positions will allow you to develop better strategies to differentiate your business.
9. Focus on Differentiation:
Identify ways to differentiate your products or services to reduce the impact of competitive rivalry and the threat of substitutes. Create unique value propositions that set your business apart from competitors.
10. Build Strong Supplier Relationships:
Maintain strong relationships with your suppliers to reduce their bargaining power. Seek long-term partnerships and collaborations, and explore alternative sourcing options to minimize supply chain disruptions.
11. Develop Customer Loyalty:
Invest in building strong customer relationships to mitigate the bargaining power of buyers. Provide excellent customer service, offer loyalty programs, and continually innovate to meet customer needs and preferences.
12. Evaluate Barriers to Entry:
Assess the barriers to entry in your industry and work to strengthen them. This could involve protecting intellectual property, securing exclusive distribution agreements, or building economies of scale to discourage new entrants.
13. Monitor Substitutes:
Keep a close eye on potential substitute products or services and be ready to adapt your offerings if necessary. Monitor changes in consumer preferences and technological advancements that could lead to new substitutes.
14. Collaborate and Form Strategic Alliances:
Consider forming strategic alliances or partnerships with other companies to strengthen your position in the market. Collaborations can help leverage complementary strengths and expand market reach.
15. Re-evaluate Periodically:
Porter’s Five Forces analysis is not a one-time exercise. Revaluate the forces periodically, especially when significant changes occur in your industry. Regular assessments will help you adjust your strategies proactively.
16. Integrate with Other Strategic Tools:
While Porter’s Five Forces analysis provides valuable insights, it is essential to integrate it with other strategic tools like SWOT analysis, PESTEL analysis, and value chain analysis. A holistic approach will give you a comprehensive understanding of your business environment.
Incorporating these steps into your strategic planning process will help you leverage Porter’s Five Forces model effectively and make informed decisions to enhance your competitive position and long-term profitability. Remember that the model is just one tool, and combining it with other analytical frameworks will lead to more robust strategic planning.
Conclusion
Porter’s Five Forces model provides a valuable framework for understanding the competitive dynamics within an industry. By assessing the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of suppliers and buyers, the threat of substitutes, and the intensity of competitive rivalry, businesses can identify opportunities and threats and develop effective strategies to thrive in their respective markets.
However, it is important to note that the model’s applicability might vary based on the specific industry and market conditions. Thus, businesses should complement Porter’s Five Forces analysis with other strategic tools and a deep understanding of their unique circumstances to make well-informed decisions and create sustainable competitive advantages.